
We used Chi-square test followed by -test for proportions to analyze the relation between hypertension status (nonhypertensive, stage 1 hypertension, and stage 2 hypertension) and both gender and BMI category. Due to the small number of participants in each group, we transformed smoking status into either a smoker (regardless of pack-year) or a nonsmoker. We also categorized both systolic and diastolic blood pressure into the groups shown in Table 2. We categorized BMI into the following groups: 18.5–24.9, 25–29.9, and 30–34.9, as shown in Table 4. We described our included sample using frequency (% proportion) for gender and mean (± standard deviation) for weight, height, systolic pressure, diastolic pressure, and BMI. We used SPSS version 21.0 (Chicago, USA). We obtained both family history of either hypertension or cardiovascular diseases (either first degree, 2nd degree, or beyond) and smoking history (measured in pack-year). They measured blood pressure for each arm twice and recorded the mean for each arm, but we only included the higher mean reading for each participant. Three of the authors (A.A., D.A., and L.F.) were previously trained on blood pressure measurement, and they were instructed to rest the participant for 5 minutes prior to the measurement, support participant’s arm, choose the correct cuff size, and place it over a bare arm. We used an upper arm automated blood pressure device (an Omron 705IT (HEM-759-E)) for blood pressure measurement, a validated blood pressure device. Body mass index (BMI) was calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared (kg/m2). We measured each participant’s height, weight, and both systolic and diastolic blood pressure at the nephrology clinics. Each eligible participant was instructed not to take any stimulant before blood pressure measurement (e.g., coffee and tea) for at least one hour. We recruited participants via an announcement published in relevant social media websites. Each participant involved in this study had a previous detailed checkup upon admission to the university the checkup included a complete history and physical examination, in addition to complete blood count and urine analysis. We only included healthy students (i.e., for the purposes of this study, those not previously diagnosed with hypertension).

We recruited university students studying at the University of Jordan in healthcare faculties, including faculty of medicine, pharmacy, and nursing.

This study was approved by our ethical committee and was conducted in concordance with the Declaration of Helsinki’s latest report. In this study, we included healthy university students from healthcare faculties looking for the frequency of hypertension and the effects of gender, BMI, smoking, and family history of both hypertension and cardiovascular diseases. Upon comparing the mean difference in both systolic and diastolic blood pressure with BMI, we found significant differences in both systolic ( 140/90 mmHg), and 13.9% were considered prehypertensive (i.e., blood pressure > 130/80 mmHg), but according to the new guidelines mentioned above, both groups are now considered hypertensive. We found significant gender differences in both systolic pressure ( = 0.003) with mean difference = 18.08 mmHg (CI: 16.13 to 19.9) and diastolic pressure ( = 0.011) with mean difference = 3.6 mmHg (CI: 2.06 to 5.14), higher in males than in females. Out of the total number of 505 participants included in this study, 35.2% have blood pressure between 130/80 and 139/89, and 13.5% have blood pressure of more than 140/90. For each participant, we performed blood pressure measurements using a previously validated device and obtained demographic data, body mass index (BMI), smoking status, and family history of both hypertension and cardiovascular diseases. We screened healthy university students ranging from 18 to 26 years of age.
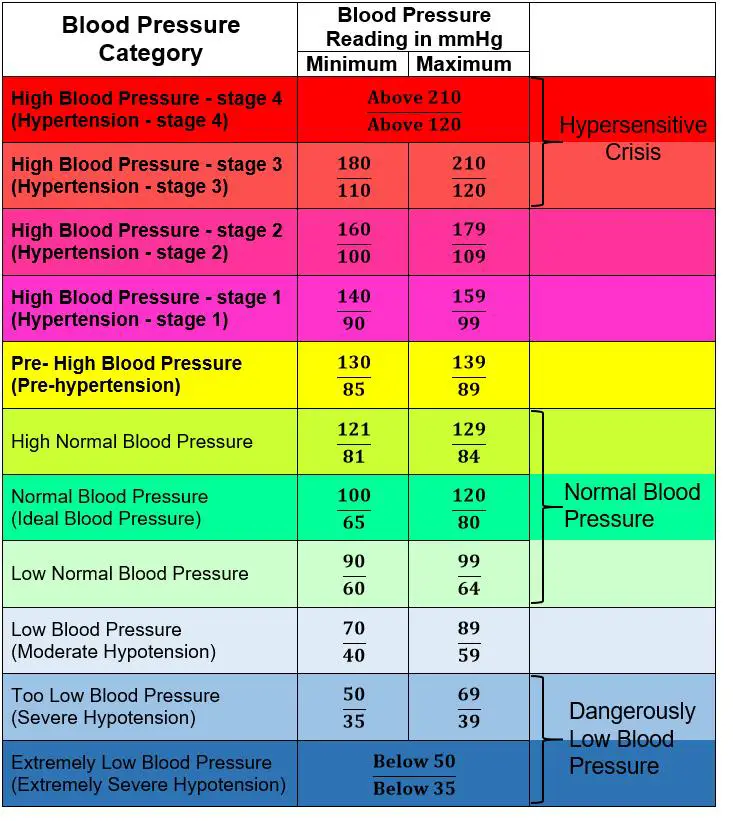
In this study, we will assess the frequency of hypertension among healthy university students and its association with gender, body mass index, smoking, and family history of both hypertension and cardiovascular diseases. Hypertension is one of the major risk factors associated with cardiovascular diseases.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
